AP Physics 1 🎡
257 resourcesSee Units
Multiple Choice Practice for Simple Harmonic Motion
Welcome to Unit 6 AP Physics 1 Multiple Choice Questions! Grab some paper and a pencil 📄 to record your answers as you go. You can see how you did on the Unit 6 Practice Questions Answers and Review sheet once you're done. Don't worry, we have tons of resources available if you get stumped 😕 on a question. And if solo study is not your thing, join a group in Hours!
Not ready to take a quiz yet? Take a look at the Intro to Unit 6.

Image courtesy of Pixabay
Facts about the test: The AP Physics 1 exam has 50 multiple choice questions (45 single-select and 5 multiple-select) and you will be given 90 minutes to complete the section. That means it should take you around 15 minutes to complete 8 questions.
The following questions were not written by College Board and, although they cover information outlined in the AP Physics 1 Course and Exam Description, the formatting on the exam may be different.
1. The period of a pendulum depends upon
A. the length of the pendulum (from pivot to the bob's center)
B. the mass of the bob
C. the weight of the bob
D. the amount which the bob is displaced form its equilibrium position
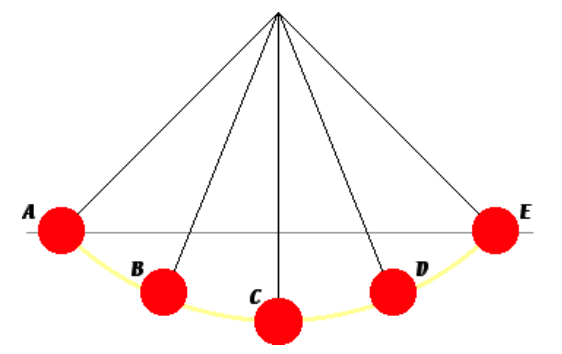
2. A mass is tied to the end of a light string. The other end of the light string is tied to a fixed point on the ceiling to create a simple pendulum. The mass (known as the bob) is pulled back and released. Once released, the bob swings to and fro. Positions A, B, C, D and E represent various locations of the bob during the course of a back-and-forth cycle. Positions A and E are locations of the bob at its two extremes. At which location is the net force experienced by the bob the greatest?
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D or E
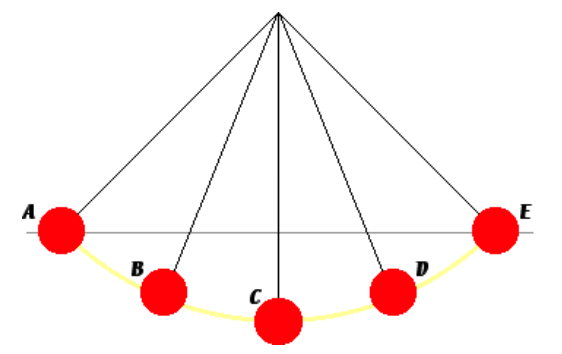
3. A mass is tied to the end of a light string. The other end of the light string is tied to a fixed point on the ceiling to create a simple pendulum. The mass (known as the bob) is pulled back and released. Once released, the bob swings to and fro. Positions A, B, C, D and E represent various locations of the bob during the course of a back-and-forth cycle. Positions A and E are locations of the bob at its two extremes. At which location(s) is/are the gravitational potential energy experienced by the bob the greatest?
A. A
B. C
C. E
D. A and E
4. The picture at the top of the diagram is of a pendulum exhibiting simple harmonic motion. The diagrams at the bottom have vector arrows. Which arrow represents the direction of the net force on the bob at location D?
A.
B.
C.
D.
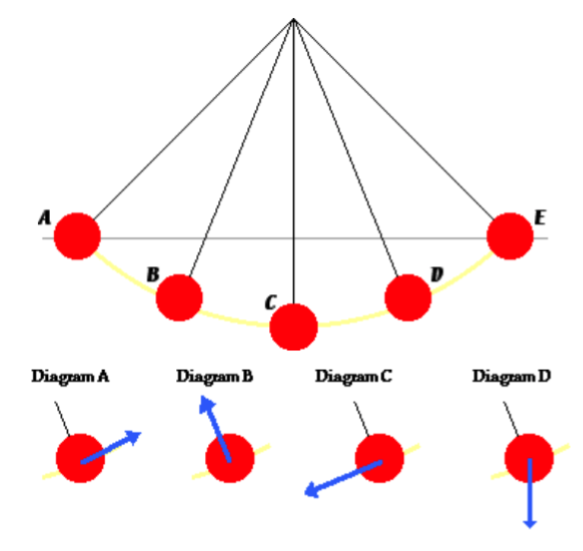
5. The picture at the top of the diagram is of a pendulum exhibiting simple harmonic motion. The diagrams at the bottom have vector arrows. Which arrow represents the direction of the velocity on the bob when at location D traveling towards E?
A.
B.
C.
D.
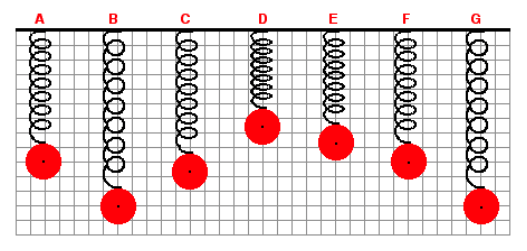
6. A mass is attached to a spring and allowed to hang vertically from a fixed support. The spring naturally stretches to position A. The mass is then pulled down to position B and released. The mass then vibrates up and down in periodic fashion. Positions C to G represent random positions of the mass over the course of several cycles of up and down motion. A background grid is shown in the graphic. Each small square on the grid measures 4 cm along its edge. At which listed position is the net force acting upon the mass equal to 0 N?
A. C
B. D
C. E
D. F
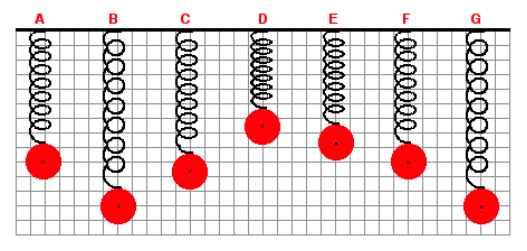
7. A mass is attached to a spring and allowed to hang vertically from a fixed support. The spring naturally stretches to position A. The mass is then pulled down to position B and released. The mass then vibrates up and down in periodic fashion. Positions C to G represent random positions of the mass over the course of several cycles of up and down motion. A background grid is shown in the graphic. Each small square on the grid measures 4 cm along its edge. The spring force exerted upon the mass is maximum when the mass is at position
A. D
B. E
C. F
D. G
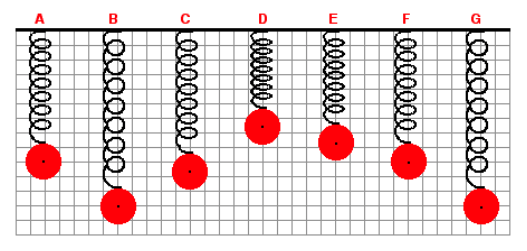
8. A mass is attached to a spring and allowed to hang vertically from a fixed support. The spring naturally stretches to position A. The mass is then pulled down to position B and released. The mass then vibrates up and down in periodic fashion. Positions C to G represent random positions of the mass over the course of several cycles of up and down motion. A background grid is shown in the graphic. Each small square on the grid measures 4 cm along its edge. Determine the amplitude of the mass while it is in SHM.
A. 3 cm
B. 12 cm
C. 24 cm
D. 48 cm
9. A body of mass 5.0 kg is suspended by a spring which stretches 10 cm when the mass is attached. It is then displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position as a function of time is approximately
A. y = .05cos9.9t
B. y=.10sin9.9t
C. y=.10cos9.9t
D. y=.10cos(9.9t+5)
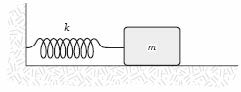
10. "A mass m = 2.0 kg is attached to a spring having a force constant k = 290 N/m as in the figure. The mass is
displaced from its equilibrium position and released. Its frequency of oscillation (in Hz) is approximately "
A. 0.01
B. 0.5
C. 1.9
D. 12
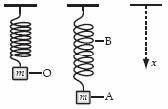
11. A weight of mass m is at rest at O when suspended from a spring, as shown. When it is pulled down and
released, it oscillates between positions A and B. Which statement about the system consisting of the spring
and the mass is correct?
A. The gravitational potential energy of the system is greatest at A.
B. The rate of change of momentum has its greatest magnitude at A and B.
C. The elastic potential energy of the system is greatest at O.
D. The rate of change of gravitational potential energy is smallest at O.
12. A block attached to an ideal spring undergoes simple harmonic motion. The acceleration of the block has its maximum magnitude at the point where
A. The speed is a minimum
B. The speed is a maximum
C. The restoring force is the minimum
D. the kinetic energy is the maximum
13. A block with a mass of 20 kg is attached to a spring with a force constant k = 50 N/m. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block when the spring is stretched 4 m from its equilibrium position?
A. 4 m/s^2
B. 6 m/s^2
C. 8 m/s^2
D. 10 m/s^2
14. A block with a mass of 10 kg connected to a spring oscillates back and forth with an amplitude of 2 m. What is the approximate period of the block if it has a speed of 4 m/s when it passes through its equilibrium point?
A. 1s
B. 3s
C. 6s
D. 12s
15. A block with a mass of 4 kg is attached to a spring on the wall that oscillates back and forth with a frequency of 4 Hz and an amplitude of 3 m. What would the frequency be if the block were replaced by one with one-fourth the mass and the amplitude of the block is increased to 9 m ?
A. 4 Hz
B. 8 Hz
C. 12 Hz
- 🙌 Time to check your answers on Unit 6 Practice Questions Answers and Review
- 🤝Connect with other students studying AP Physics with Hours
Browse Study Guides By Unit
👟Unit 1 – Kinematics
🌀Unit 2 – Dynamics
🚀Unit 3 – Circular Motion & Gravitation
⚡️Unit 4 – Energy
⛳️Unit 5 – Momentum
🎸Unit 6 – Simple Harmonic Motion
🎡Unit 7 – Torque & Rotational Motion
💡Unit 8 – Electric Charges & Electric Force
🔋Unit 9 – DC Circuits
🔊Unit 10 – Mechanical Waves & Sound
👉AP Physics Essentials
🧐Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
✍️Free Response Questions (FRQs)
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.