E
Edmund Scanlan
E
Edmund Scanlan
AP Human Geography 🚜
320 resourcesSee Units
Fertility Rates
Developed areas, like Europe, North America, and Australia, have more educated women and lower fertility rates. A higher percentage of women in the workforce leads to lower TFR, which leads to lower natural increase rates.
The Natural increase rate is the crude birth rate (amount of babies born per 1000 people in a year) minus the crude death rate (amount of people that die per 1000 people in a year).
In developing areas, like Sub-Saharan Africa, and South and Southeast Asia, women have fewer years of schooling and higher fertility rates. They also use subsistence farming, where more children can be advantageous to help farm. These reasons lead to higher natural increase rates.
There are many reasons as to why a country's fertility rate would change. A main large cause of a decrease in fertility rates is more education for women and easier access to family planning and reproductive health services (like contraceptives). There are also a lot of social causes, like a change in population demographics, or political instability.
There are a lot of cultural and social norms in developing countries that lead to larger family sizes, meaning that a larger family could be seen as economic security or higher social status. At the same time, more children mean more workers for the family farm, and generally, that is a family's income so they benefit by having more people working.
Mortality
Mortality varies in developed and developing countries. Developed areas have better hospitals, healthcare, and more access to birth control, which leads to lower infant mortality rates, which is the total number of deaths of children aged 0-1 in a year. Because of this children are more likely to grow to adulthood, which causes women to have fewer children.
Developing countries also have higher infant mortality rates, because of lack of healthcare and worse sanitary conditions. Birth control is less available. Because of this the TFR in some Sub-Saharan African countries is over 5!
Migration
Migration also varies in developed and developing countries. In the developed world, they have net-in migration, because people are coming to the country for better economic conditions.
The reason that the United States population continues to rise is because of net-in migration. The blue countries in this map represent places that have an increasing population due to migration. Most of these countries are developed, however, a few developing countries in Africa and Asia also experience a growing population due to migration.
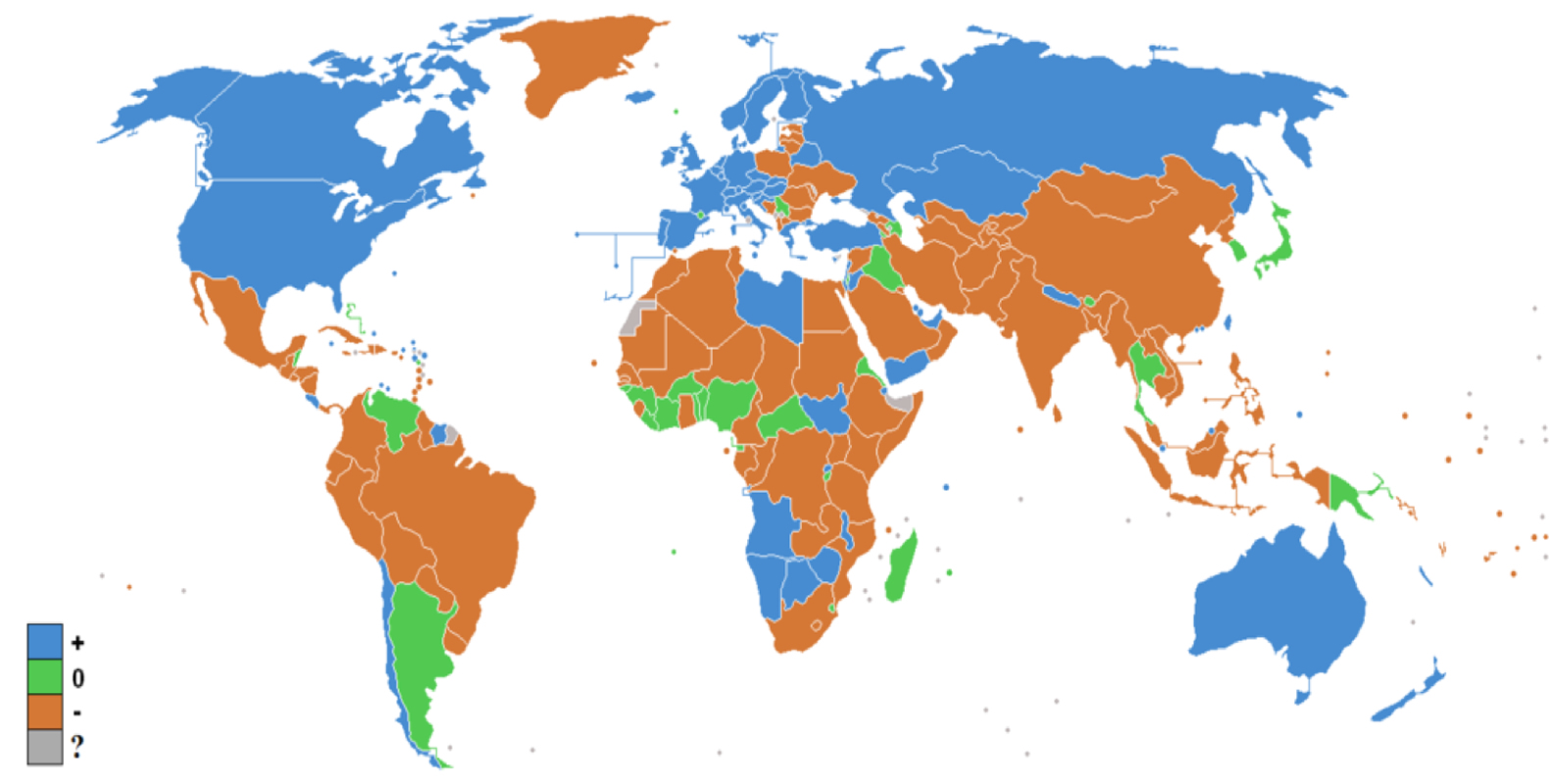
In the developing world they have a net-out migration because people are leaving to seek better job opportunities internationally. Some also leave because the population of the country continues to rise, which can lead to overpopulation and overcrowding in urban areas.
Besides Natural Increase Rate, geographers also use doubling time, which is the number of years needed for a population to double, assuming the NIR stays constant.
However, NIR can change drastically for a number of reasons. War, famine, or political instability in a country can cause net-out migration to go up, or the TFR to drop. While those same factors in a bordering country can have the inverse effect.
Causes of Migration
Social
A social example is chain migration. That is when people move to a specific location because members or relatives of a similar nationality have already migrated there. This is very common as people typically try to move to places where they know other people and have an existing connection. It also leads to ethnic enclaves, like Chinatown. Ethnic enclaves are neighborhoods or communities within a larger region that are predominantly inhabited by a particular ethnic group.
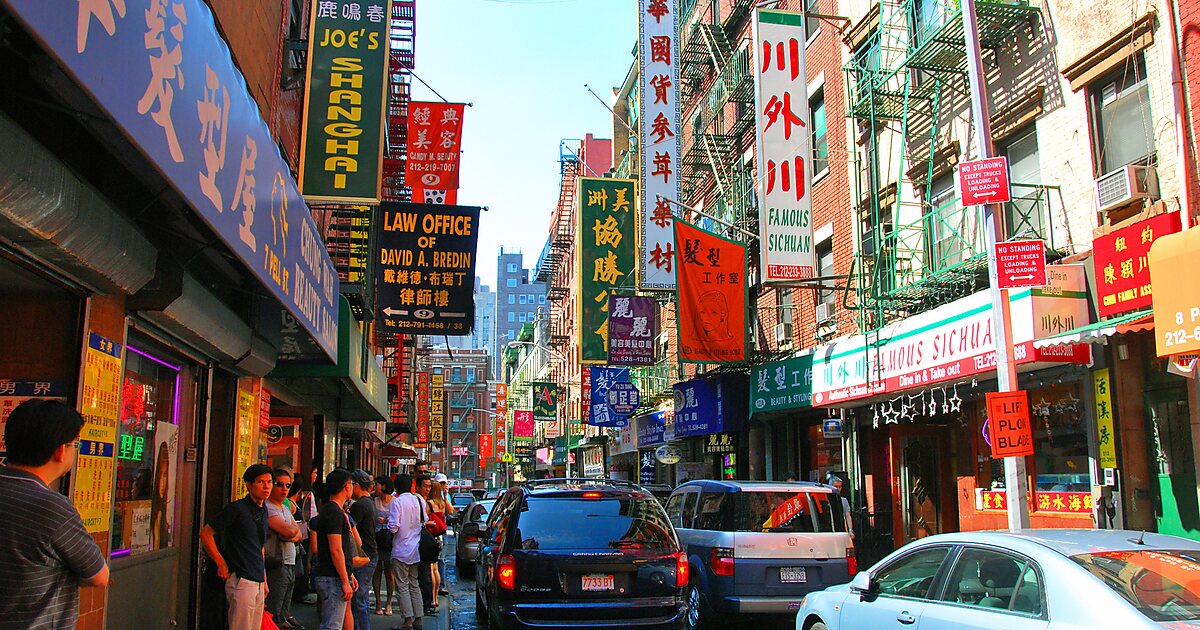

photo taken from google images
Cultural
Cultural reasons people may migrate is because of their religion, beliefs, sexual orientation, or oppression of their ethnicity or race. This may be for forced or voluntary reasons.
People may choose to live in places that are religious centers like Israel, Mecca, or Salt Lake City (voluntarily). On the other hand, you could move somewhere for acceptance. For example, a person may want to move to somewhere more LGBTQ friendly.
Examples of forced migration due to culture are the Jewish diaspora, the Protestant Reformation, and the forced relocation of Native American tribes in the United States.
Political
There are two types of political migration. Voluntary migration is the permanent movement of people by choice. Forced migration is the permanent movement of people, who are compelled to move for different reasons. Sometimes the government is oppressing people, or they will move because of political instability or outright warfare. A lot of people are currently migrating out of Ukraine due to the current conflict existing there. This is a good example of forced migration.
Economic
Economics is the number one reason why people move to or within a country that provides more job opportunity.
This can be international, from one country to another, intra-national, within the same country, interregional, from one region of a country to another, or intraregional, within the same region of a country.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Decoding Population Pyramids
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🗺Unit 1 – Thinking Geographically
👪Unit 2 – Population & Migration
🕌Unit 3 – Cultural Geography
🗳Unit 4 – Political Geography
👨🌾Unit 5 – Agriculture & Rural Land-Use
🌇Unit 6 – Cities & Urban Land-Use
💸Unit 7 – Industrial & Economic Development
✏️Frequently Asked Questions
🧐Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
✍️Free Response Questions (FRQ)
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.