Mary Valdez
Haseung Jun
John Mohl
Dalia Savy
Mary Valdez
Haseung Jun
John Mohl
Dalia Savy
AP Psychology 🧠
334 resourcesSee Units
This unit is about motivation. It identifies and applies motivational concepts to understand behavior of humans and animals🧑🤝🧑🐻. It talks about the strengths and weaknesses between theories and the most basic primary needs: physiological, social, and sexual.
Motivational Concepts
Motivation is something that directs a behavior. For example, if you want to get a good grade on the AP Psych exam in May, you are motivated to study 💯 You're probably very familiar with motivation, but it goes deeper than you think and basically exists in every action you do.
Before going through the theories, let's discuss some vocab terms:
- Instincts are behaviors that occur unconsciously because they usually just "feel right."
- Incentives drive us toward or away from the behavior we want. The incentive could either be a positive stimulus or a negative stimulus, but either way, it impacts our behavior🚶
- Intrinsic motivation is when you are doing something for yourself. An example of this would be reading just because you love to read ❤️📖
- Extrinsic motivation is when you are doing something for an external factor. Using the above example, if you read just to fulfill a summer assignment ✔️📖, you were extrinsically motivated.
- Having intrinsic motivation is stronger and drives you farther since it is something you, yourself, are genuinely interested in.
- The overjustification effect is when an external factor decreases one's intrinsic motivation to complete a certain task. For example, if you began to learn French on your own time and then came across a really good job offer that requires French, you may now begin to learn French just for the job, rather than yourself💰
- Achievement motivation is one theory that states our desires to master complex stuff and reach personal goals is our motivations. So even without skills, benefits or knowledge, we are motivated to challenge ourselves. Now obviously this does vary from person to person, but it is true that our motivation does drive us to do crazy stuff!
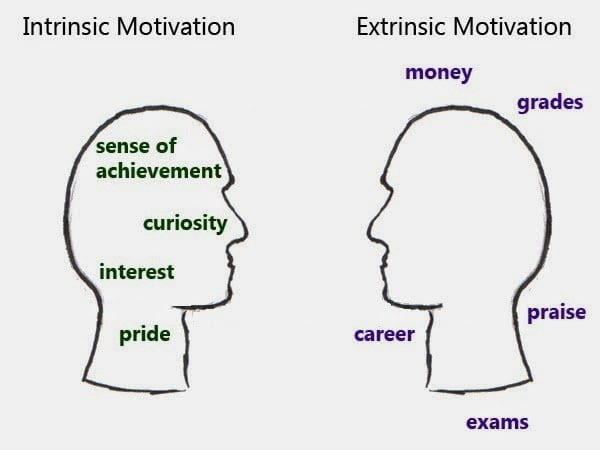
Image Courtesy of Sites at Penn State.
- Self-Efficacy:
- High self-efficacy is the belief that someone can complete a task successfully. This usually goes hand in hand with high intrinsic motivation and accepting challenges along the way.
- Low self-efficacy is being uncertain that you can master a task and goes hand in hand with low intrinsic motivation. You don't feel as interested in learning the task, so you are unsure if you will be good at it. Having low self-efficacy leads to giving up and avoiding obstacles.
Different Theories
Many different theories about motivation developed over time. Let's discuss them!
Instinct Theory (evolutionary)
This theory has to do with Charles Darwin's principle of natural selection that stated that those that are best adapted to their environments are most likely to mate and survive. Therefore, the motivation in this theory is to survive and we, as well as animals, adapt behaviors that help us live 💕
| Example | Strength of Theory 👍 | Weakness of Theory 👎 |
| All babies display innate reflexes like rooting and sucking | It helps explain similarities due to our ancestral past. | It helps explain animal behaviors better than human behaviors. |
Drive-reduction Theory (biological)
This theory focuses on how our inner pushes and external pulls interact to drive our behaviors.
- Push Factors: Motivate us to get away from bad things
- Pull Factors: Motivate us to work toward good things
We have our need, drives, and behaviors. Our physiological needs create a tensional state that motivates an organism to satisfy that need by doing a certain behavior.
By doing this behavior, we should reach homeostasis, which is a steady internal state.
| Example | Strength of Theory👍 | Weakness of Theory👎 |
| When you need food, you become hungry, and then you cook yourself something to make the feeling of hunger go away. | It explains our motivation to reduce arousal by meeting basic needs, hunger, or thirst. | It doesn't explain why some motivated behaviors increase arousal. |
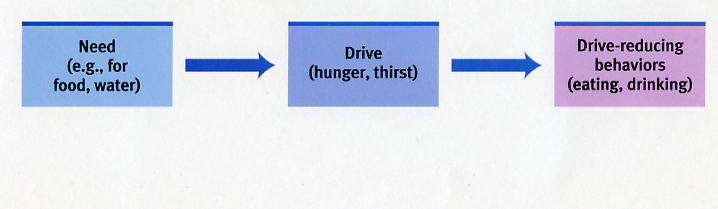
Image Courtesy of Myers' AP Psychology Textbook 2nd Edition.
Optimal Arousal Theory
The optimal arousal theory focuses on finding the right level of stimulation. An organism tries to find behaviors that actually increase arousal because everything else bores them.
| Example | Strength of Theory👍 | Weakness of Theory👎 |
| Being bored and getting yourself into trouble just because you needed to find something to do. Another example is "Curiosity kills the cat" and you just wanna try something new that excites you! | It explains that motivated behavior may increase or decrease arousal. | It doesn't explain our motivation to address our more complex social needs. |
Yerkes-Dodson law
The Yerkes-Dodson law suggests moderate arousal can lead to optimal performance. With this being said, you've probably experienced the law in real life.
If you were ever way too relaxed 😴 when taking an exam or way too stressed 😟, I bet you noticed a decrease in your exam performance. However, if you are moderately aroused so much that you are aware and alert, you will obtain a higher score.
Tip—The Yerkes-Dodson Law is very different from the optimal arousal theory. It focuses more on the relationship between performance and arousal.
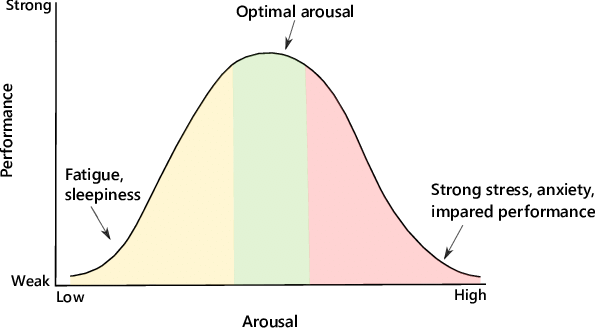
Image Courtesy of ResearchGate.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow came up with a theory based on needs. The first level of needs focuses on fulfilling basic, physiological needs. Once they are met, the focus shifts to more cognitive and abstract needs.
From the bottom to the top, the pyramid reads:
- 💧🍔Physiological needs (air, food, and water)
- 🏠Safety (shelter, place to live)
- 💕Belongingness (love, a connection with someone or something)
- 😍Self esteem (loving yourself)
- 🏆Self actualization (achieving any goal you set your mind to).
- Reaching self-actualization is nearly impossible. To do this, you would have to find meaning beyond yourself.
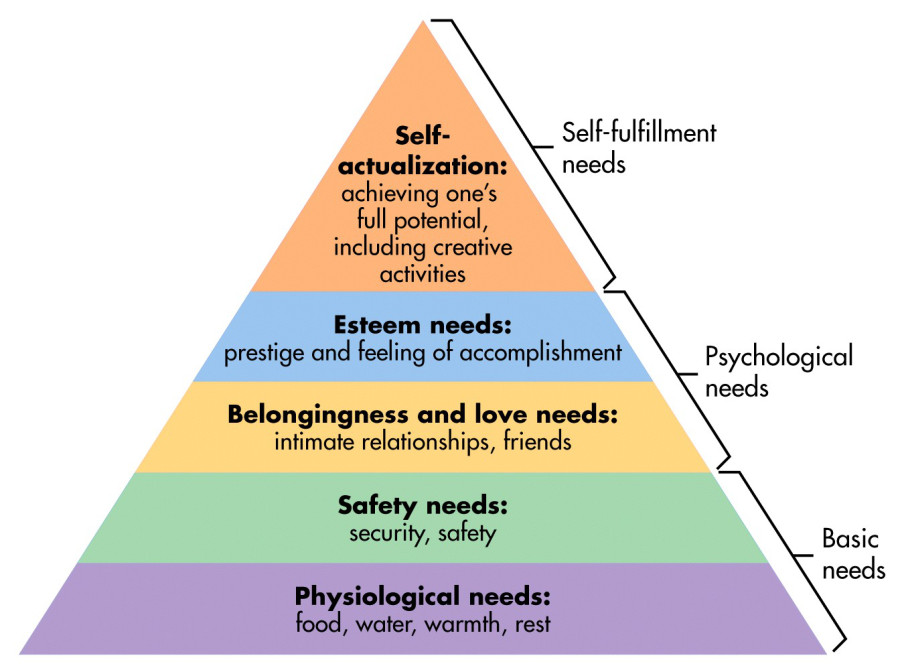
Image Courtesy of Simply Psychology.
| Strength of this Theory | Weakness of this Theory |
| It incorporates the idea that we have levels of various needs. | The order of needs may change depending on the circumstance of the person. |
Motivations
Eating
Ever felt that huge urge to eat those Oreo late at night? Well that's a motivation of hunger, which happens simply because we need food. Or is it that simple?? Hunger motivations actually involved biological, psychological, and social factors.
Our brain plays the biggest role in hunger. The hypothalamus controls body chemistry. So when it's time for you to eat, the lateral hypothalamus activates, causing you to eat. Then you are getting pretty full from eating 5 bags of Oreos on your own. That's when the ventromedial hypothalamus kicks in, causing you to stop eating. If either part is damaged, you'll either never eat because you never feel hungry or you'll never stop eating because you don't feel satisfied. Both situations are kinda horrifying 😖.
So how does the hypothalamus decide when we need to feel hungry and full? Well the set-point theory states that the hypothalamus wants to maintain a certain body weight. So when your weight drops, it'll tell you to eat more and lower the metabolic rate, which is how quickly your body uses your energy.
But it's not solely the hypothalamus that gets to decide everything. there's also something called the Garcia effect, which states that there are certain foods that make you more hungry. If you have bad memory of eating hot dogs and throwing up, you might not feel too hungry around hot dogs as you would to Oreos. Culture and background can also play a similar effect.
Sexual Motivation
Like hunger, sexual motivations have biological and psychological properties.
The physical sexual response cycle is as follows:
- initial excitement - respiration and heart rate increase
- plateau phase - respiration and heart rate continue at an elevated rate
- orgasm - rhythmic genital contractions, euphoria
- resolution phase - respiration and heart rate return to normal
Sexual desire comes from psychological factors too. Elevation in levels of hormones or erotic material are good examples.
Social Motivation
Basically, this means you want to succeed. You want to challenge yourself and reach your goals. This is called achievement motivation. This is different from optimum arousal because it's not about only being motivated to seek, it's more about meeting a high achievement goal.
🎥 Watch: AP Psychology—Motivations
🏆 Trivia—Motivations
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🔎Unit 1 – Scientific Foundations of Psychology
🧠Unit 2 – Biological Basis of Behavior
👀Unit 3 – Sensation & Perception
📚Unit 4 – Learning
🤔Unit 5 – Cognitive Psychology
👶🏽Unit 6 – Developmental Psychology
🤪Unit 7 – Motivation, Emotion, & Personality
🛋Unit 8 – Clinical Psychology
👫Unit 9 – Social Psychology
🗓️Previous Exam Prep
📚Study Tools
🤔Exam Skills

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.